Introduction
Hair loss is an extremely common condition that can affect both men and women. According to research, up to 50% of men and 25% of women will experience noticeable hair loss by the age of 50. While genetics play a major role, other factors like stress, medications, illness, and environmental exposures can also trigger hair loss and thinning.
This article provides an overview of the most common types, causes, and treatments for hair loss. We’ll cover everything from lifestyle changes and home remedies to medical therapies like minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants. You’ll also learn ways to cope with the emotional impact of losing hair and when it’s time to see a dermatologist. The goal is to give you a comprehensive guide to understanding why you may be losing hair and the most effective solutions.
Types of Hair Loss
The most common types of hair loss include:

- Androgenetic alopecia – Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most common type of hair loss. It’s caused by hormones and genetics, and results in a receding hairline and/or thinning hair on the crown of the head. This type of baldness is permanent, but treatments are available to slow further hair loss.
- Alopecia areata – This causes patchy hair loss, often starting with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition and the cause is unknown, although it often self-resolves. The hair may regrow fully within a year.
- Telogen effluvium – This refers to excessive daily shedding of hair resulting in thinning. It’s often temporary and caused by factors like stress, poor nutrition, hormonal changes, or medical conditions. With treatment, the hair typically regrows once the trigger is addressed.
Common Causes
Hair loss can be caused by a variety of factors. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Heredity and genetics – Male and female pattern baldness is the most common type of hair loss. It runs in families and is caused by genetics. If your parents or grandparents experienced hair loss, you may have a predisposition for it as well. The mechanisms behind genetic hair loss are related to the androgen (male) hormones.
- Hormonal changes – Hormone imbalances and fluctuations can lead to temporary hair loss. Examples include pregnancy, childbirth, discontinuing birth control pills, thyroid problems, and menopause. The hormonal changes shock the hair follicles and can force them to go into resting phase temporarily.
- Medical conditions – Conditions like alopecia areata, scalp infections, thyroid disease, lupus, iron deficiency anemia, eating disorders, and other illnesses can cause hair loss. The hair loss usually stops when the underlying condition is treated.
- Medications – Certain prescription drugs, like those used to treat cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems and high blood pressure, can cause hair loss as a side effect. When the medication is stopped, normal hair growth resumes.
- Stress – High levels of physical or emotional stress can cause temporary hair loss. Events such as childbirth, divorce, loss of a job, loss of a loved one, surgery, or a serious illness may shock the body and hair follicles, resulting in shedding and hair loss. Once the stressor is removed and the body recovers, normal hair growth typically returns.
The common thread between these causes is that they push hair follicles into the resting phase, resulting in hair fall or breakage. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause is key to stopping hair loss.
Diagnosing Hair Loss
There are several methods doctors use to diagnose the underlying cause of hair loss. This is an important step, as the treatment will depend on the specific type and cause of hair loss.
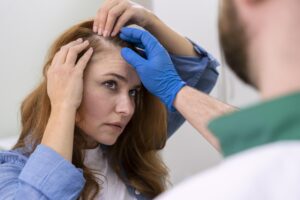
- Physical Exam – The first step is usually a physical exam. The doctor will thoroughly examine the hair and scalp to check for any visible signs of infection, inflammation, scarring, or other abnormalities. They may use a special magnifying lens to get a close look at individual hairs and follicles. This can help determine if the hair loss pattern matches male- or female-pattern baldness or if it indicates another condition.
- Pull Test – Doctors may do a pull test, gently pulling small batches of hair to see how many come loose in the fingers. More than 6-8 hairs coming out could indicate active shedding.
- Biopsy – A biopsy involves taking a small sample of scalp skin and examining it under a microscope. This can reveal issues like infections, inflammation, or hormonal effects on the hair follicle. It can also determine whether follicles have been replaced with scar tissue, indicating permanent hair loss.
- Blood Tests – Blood work can detect many internal causes of hair loss like nutritional deficiencies, thyroid problems, and hormone imbalances. For example, blood tests can check iron levels, vitamin D, zinc, and hormone levels like estrogen in women and testosterone in men. Any hormonal abnormalities or nutrient deficiencies contributing to hair loss can then be addressed.
Getting an accurate diagnosis through these methods is important before starting treatment for hair loss. It ensures you are addressing the specific underlying cause with the proper remedies and course of action.
Conventional Treatments
There are a few medications and procedures commonly used to treat hair loss:
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical solution that helps stimulate hair growth. The exact mechanism of how it works is not fully understood, but it appears to enlarge hair follicles and prolong the growth phase of hair. Minoxidil is available in 2% and 5% solutions, with the 5% version being more effective. It must be applied to the scalp twice daily and works best for hereditary hair loss. About 40% of individuals using minoxidil regrow some hair, and it also helps slow further thinning. It can take 3-6 months to see results.
Finasteride
Finasteride is an oral medication that blocks the hormone DHT, which causes thinning in those with male and female pattern baldness. By inhibiting DHT, finasteride stops further hair loss and promotes regrowth in about 66% of men who use it. For best results, it must be taken daily. Finasteride requires a prescription and is sold under brand names like Propecia and Proscar.
Laser Devices
Low-level laser light therapy is sometimes used to stimulate hair follicles. Handheld devices are combed through the hair on a regular basis. The lasers target the cells in hair follicles to enhance metabolism and cellular activity. This treatment can help stop hair loss and potentially regrow hair when used on its own or in combination with other therapies. However, results vary greatly from person to person.
Natural Remedies
There are several natural remedies that may help treat hair loss, often with fewer side effects than conventional treatments. Many people find success using a combination of natural remedies alongside other treatments.

Nutritional Supplements
Certain vitamins and minerals are linked to hair growth and retention. Two of the most popular supplements for hair loss are:
- Biotin – This B vitamin helps produce keratin, which hair is made of. Take 2.5-5mg of biotin daily. Look for supplements specially formulated for hair health.
- Zinc – Zinc contributes to protein synthesis needed for hair growth. The recommended daily dose is 8-11mg for women and 11mg for men.
Essential Oils
Essential oils are touted for stimulating circulation in the scalp and promoting healthy hair. Two oils to try are:
- Peppermint oil – Massage diluted peppermint oil into the scalp. It provides a cooling sensation that stimulates blood flow.
- Rosemary oil – Rosemary oil improves hair growth. Add a few drops to your shampoo or massage it into your scalp.
Scalp Massage
A scalp massage can increase circulation and reduce stress hormones that lead to hair loss. Use your fingertips to massage your scalp in circular motions before bed or while shampooing in the shower. Apply light to medium pressure and focus on any areas of sensitivity.
Consistently using these natural remedies may help combat hair loss, especially when paired with a healthy diet, manageable stress levels, and other hair-supporting habits. Be patient when trying natural treatments, as noticeable improvements in hair growth can take 2-4 months. Always consult your doctor before changing medications or supplements.
Hair Transplants
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that moves hair follicles from a part of the body called the ‘donor site’ to a bald or balding part of the body known as the ‘recipient site’. It is primarily used to treat male pattern baldness.
The most common donor sites are the back and sides of the scalp. During a hair transplant, a dermatologist or cosmetic surgeon will remove a strip of skin containing hair follicles from the donor site. The strip is then divided into hundreds of tiny grafts, each containing just a few hairs.
The surgeon creates small holes or slits in the scalp at the recipient site and carefully implants each graft. New hair should begin to grow from the transplanted follicles within a few months.
Success rates for hair transplantation are generally high. Around 90% of transplanted hair follicles will take hold and begin to regrow permanent hair. However, some grafts may not survive the transplant process. Multiple procedures are often needed to achieve the desired fullness, especially for extensive baldness.
On average, a single hair transplant procedure costs between $4,000-$15,000. The exact cost depends on the number of grafts being transplanted. One graft contains 1-4 hairs. Most patients require between 1,000-2,000 grafts for a full transplant. Additional sessions will incur additional costs.
Hair transplantation is considered a relatively safe procedure when performed by an experienced surgeon. Risks include bleeding, infections, and poor hair growth. Swelling, pain, and scarring at the transplant sites are common but usually temporary side effects.
Coping with Hair Loss
Losing your hair can be an emotionally difficult experience. Here are some tips that may help you adjust both physically and mentally while coping with hair loss:

Hairstyle and Grooming Tips
- Consult a stylist to find flattering hairstyles and cuts that will make thinning hair less noticeable. Shorter cuts often work better.
- Try using volumizing shampoos and sprays to give the appearance of fuller hair.
- Use soft scrunchies, loose hair ties, and gentle brushes to avoid damage and breakage to fragile hair.
- Consider trying scalp makeup like keratin fibers to conceal visible thinning spots.
- Grow facial hair like a beard or mustache to balance hair loss on the scalp.
Emotional Support Resources
- Seek counseling or join a support group to help handle the emotional impact in a healthy way.
- Practice self-love, self-acceptance, and body positivity when you feel self-conscious about hair loss. Recognize that beauty comes in many forms.
- Lean on understanding family and friends for reassurance when you need it.
- Use relaxation practices like meditation and yoga to reduce stress, which can aggravate hair loss.
Embracing Natural Beauty
- Take inspiration from public figures and models who embrace natural hair loss with grace and confidence.
- Avoid harmful hair thickening products or procedures and learn to feel comfortable in your own skin.
- Remind yourself that hair does not define you or diminish your inner beauty and talents.
- Focus on positive attributes like compassion, intelligence, and kindness that make you beautifully unique.
Preventing Further Loss
While hair loss can sometimes feel inevitable, there are steps you can take to help slow or stop additional loss. The key is early intervention before the follicles sustain too much damage and implementing a proactive hair care routine.
Avoid damaging styles and products:
Certain hairstyles that pull tightly on the hair, like tight ponytails and braids, can put excess tension on hair follicles over time and lead to traction alopecia. Chemical treatments like perms, relaxers, or dyes with harsh ingredients can weaken and damage hair as well. Limit use of heated styling tools that get very hot and cause dryness.
Gentle scalp massages:
Massaging the scalp with gentle, circular motions helps increase blood flow which provides nutrients to hair follicles for growth. Using a few drops of peppermint or rosemary oil while massaging can offer additional benefits.
Protect hair from sun damage:
Use protective styles or hats when spending time in the sun. UV rays can dry out hair and the scalp. Apply products with UV filters to offer an extra layer of protection if hair will be exposed.
Eat a nutritious diet:
Getting enough protein, iron, zinc, vitamin C and vitamin D promotes overall hair health and growth. Consider supplements if diet is lacking certain nutrients tied to hair growth.
Manage stress levels:
High stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to excess shedding. Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, journaling or talking to a friend can help.
Use gentle hair products:
Look for shampoos, conditioners and styling products that are sulfate-free, paraben-free and made for damaged or thinning hair. Avoid rubbing hair vigorously with towels. Let hair air dry when possible.
Address medical conditions:
Managing conditions like thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, anemia, or low iron that can contribute to hair loss allows treatments to work better.
When to See a Doctor
If you are experiencing sudden, rapid, or patchy hair loss that does not seem linked to any of the common triggers, it is important to make an appointment with your doctor.
Unexplained hair loss that happens very quickly is not normal and may indicate an underlying health condition that requires medical attention. Thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, skin conditions like ringworm, and iron or vitamin deficiency can all cause sudden hair shedding.
It’s also advisable to see your doctor if you notice hair loss along with other symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, headaches, skin rash or changes. Hair loss with other symptoms could mean there is a bigger issue affecting your health. Your doctor can help determine the cause and treat accordingly.
You should also make an appointment if you have been trying natural remedies and over-the-counter treatments for more than 6 months without improvement. While natural methods can be effective for some, others may require prescription medications or procedures under a doctor’s care.
Don’t suffer extreme hair loss in silence – see your doctor for an evaluation. They can discuss treatment options that may help reduce hair loss and stimulate regrowth. The sooner it is addressed, the better chance you have of restoring your hair to its former thickness and fullness.


